Metrion’s hiPSC-derived cardiomyocyte assay is a higher-throughput, 96-well plate-based system designed to assess changes in action potential morphology, which is a key indicator of cardiac function. The assay can be used to evaluate both acute and chronic exposure to compounds, providing comprehensive safety pharmacology and toxicology data over a range of exposure durations (24 hours or greater). This is especially important for detecting chronic toxicities that may not be apparent during short-term testing.
Highly cost-efficient cardiomyocyte assay
The 96-well plate format makes the assay highly cost-efficient and suitable for higher-throughput screening.
- Ideal for rapidly evaluating larger numbers of compounds.
- The system’s ability to provide data on action potential morphology is vital for assessing how compounds interact with ion channels and their potential to disrupt normal cardiac function, which could lead to adverse events such as arrhythmias.
- Simultaneous high-resolution measurement across 96 well plate at 10,000 Hz
- Recordings using voltage-sensitive dye that deliver patch-clamp equivalent quality
- Multiple endpoints evaluated (APD20/50/90, rise time, beat rate, triangulation)
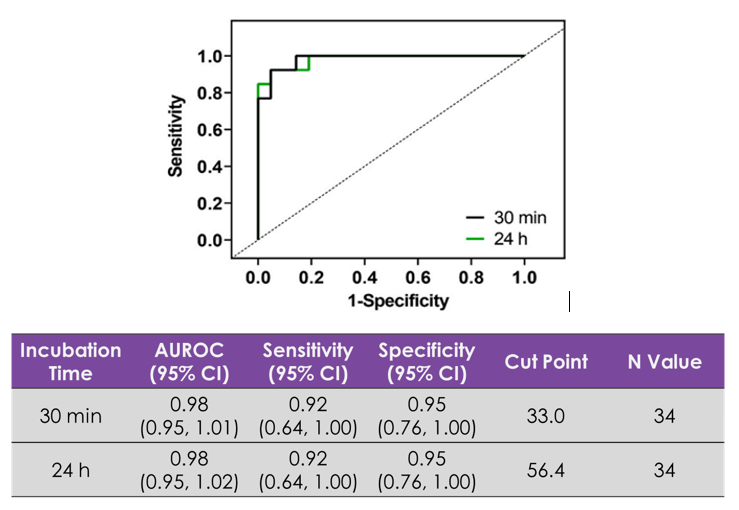
- Measurement of acute (30min) and chronic (24h/48h) effects
- Predicts clinical exposure associated with 10ms QTc prolongation
- Defines exposure associated with QRS probability
- Highlights unknown acute/chronic toxicity
The assay is aligned with current International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) S7B guidelines for non-clinical cardiac safety testing and adheres to the principles outlined in the FDA Modernization Act 2.0. These guidelines are designed to ensure that drugs are evaluated in ways that are relevant to human health, improving the overall safety and efficacy of new therapeutics. Read about the need to embrace the future of preclinical drug discovery safety.
A critical feature of Metrion’s hiPSC-derived cardiomyocyte assay is its ability to assess the impact of compounds on action potential morphology. Changes in the shape and duration of the cardiac action potential are key indicators of potential toxicity or arrhythmia risk. By examining how compounds affect ion channel activity and their interactions with critical cardiac proteins such as hERG, researchers can gain insight into whether a compound might cause harmful effects on the heart.
Recordings using voltage-sensitive dye (VSD) with quality equivalent to patch-clamp are valuable for assessing cardiovascular risk in drug discovery. They provide a high-fidelity, high-throughput alternative to traditional electrophysiology techniques.
VSD-based recordings offer:
- Non-invasive, high-resolution measurements of membrane potential changes across a large number of cells or wells simultaneously, enabling faster and more efficient cardiac safety screening.
- Precise detection of drug-induced effects on cardiac ion channels, such as hERG (IKr), NaV5, and CaV1.2, which are critical for evaluating proarrhythmic risk.
- The ability to achieve patch-clamp-equivalent data quality enhances predictive accuracy, reducing false negatives and late-stage failures, and supports safer drug development with improved preclinical-to-clinical translation.
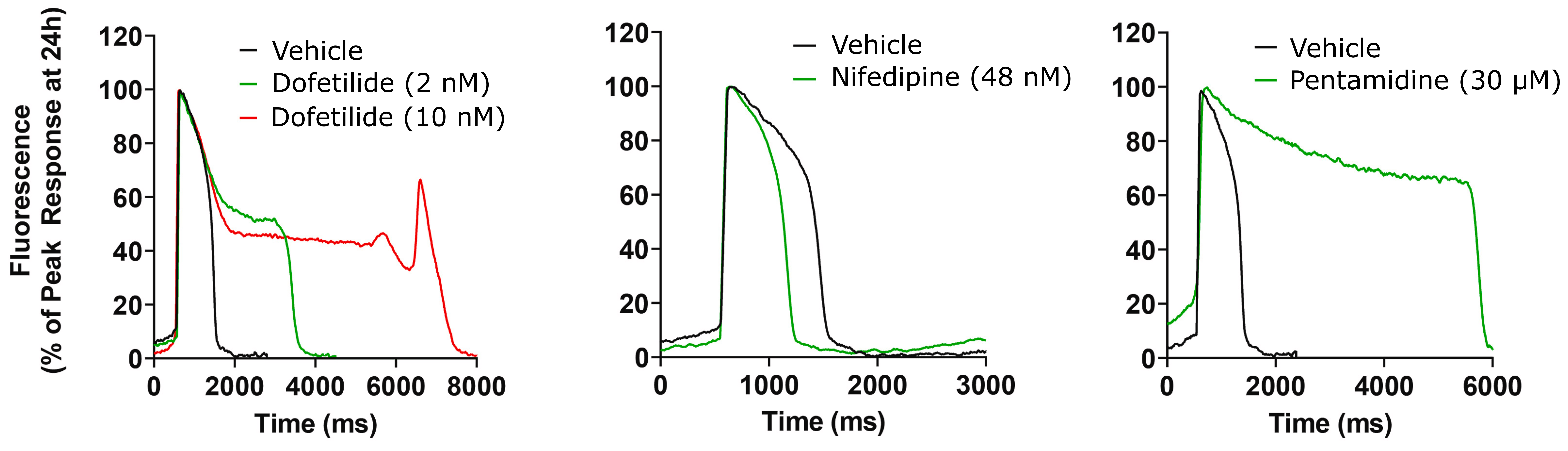
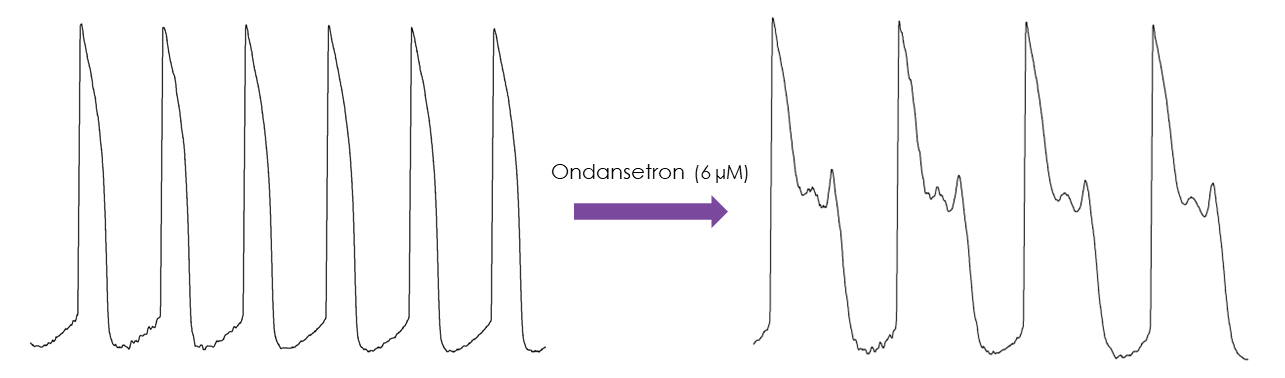
Figure 1. Representative traces from the assay clearly demonstrate how selective ion channel blockers or hERG trafficking block agents influence the action potential morphology of hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes. This enables detailed analysis of how different compounds might cause changes in the duration and characteristics of the action potential, providing a clearer understanding of their potential risks before clinical testing. Peter Kilfoil, Shuyun Lily Feng, Asser Bassyouni, Tiffany Lee, Derek Leishman, Dingzhou Li, David J. MacEwan, Parveen Sharma, Eric D. Watt, Stephen Jenkinson, Characterization of a high throughput human stem cell cardiomyocyte assay to predict drug-induced changes in clinical electrocardiogram parameters, European Journal of Pharmacology, Volume 912, 2021.
 Metrion’s human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived cardiomyocyte assay represents an advanced and cutting-edge tool that provides for early cardiac derisking in drug discovery. This revolutionary model can play a vital role in the evaluation of novel pharmaceutical compounds during the early stages of drug development by enabling researchers to predict potential cardiac risks with higher accuracy and efficiency.
Metrion’s human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived cardiomyocyte assay represents an advanced and cutting-edge tool that provides for early cardiac derisking in drug discovery. This revolutionary model can play a vital role in the evaluation of novel pharmaceutical compounds during the early stages of drug development by enabling researchers to predict potential cardiac risks with higher accuracy and efficiency.