Advancing NaV1.9 electrophysiology for drug discovery
hNaV1.9 monoclone selection workflow for neuropathic pain research
Figure 1 - Monoclonal CHO-hNaV1.9 cell lines were generated using dilution cloning and screened using a FLIPR Penta system. Positive clones were subsequently screened using a Qube 384 automated patch clamp platform, with the best further validated using manual patch clamp.
Validating hNaV1.9 expression using manual patch clamp

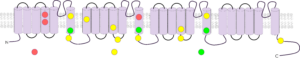
Figure 2 - Representative current traces and IV analysis of hNaV1.9, recorded using the whole-cell manual patch clamp technique (A). Conductance/voltage plot for hNaV1.9 (B). hNaV1.9 currents were inhibited using the NaV channel blocker, TC-N 1752, at 3 µM (C). The selected monoclone was confirmed to express hNaV1.9 and was progressed to assay development on the Qube automated electrophysiology platform.
Optimising automated recording conditions of hNaV1.9 via altering GTPγS concentration
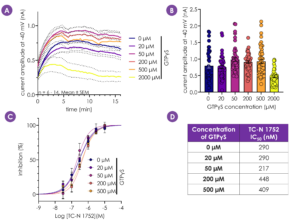
Figure 3 - Enhanced G-protein signalling has been shown to potentiate NaV1.9 current amplitudes6. Addition of up to 500 µM intracellular GTPγS resulted in larger hNaV1.9 currents, whilst 2000 µM GTPγS reduced hNaV1.9 current amplitude (A,B). Importantly, GTPγS concentration did not alter hNaV1.9 pharmacology (C,D). A concentration of 200 µM was selected for future experiments.
Biophysical assessment of hNaV1.9 using automated patch clamp technology
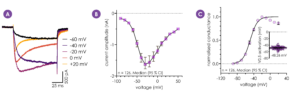
Figure 4 - NaV1.9 channels have distinct biophysical properties compared to the other NaV isoforms1 (A). The IV relationship (B) and conductance (C) of hNaV1.9 currents recorded from 126 Qube 384 multi-hole wells were consistent with the known characteristics of native hNaV1.9 and data obtained using the manual patch clamp technique.
Pharmacological assessment of hNaV1.9 using automated patch clamp for drug discovery
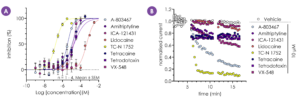
Figure 5 - A Qube 384 assay was successfully developed to screen a selection of NaV inhibitors with a range of potencies and isoform selectivity against hNaV1.9. Calculated IC50 values (µM): A-803467 – 3.51, Amitriptyline – 18, ICA-121431 >30, Lidocaine – 460, TC-N 1752 – 0.2, Tetracaine – 11.5, TTX – 18.7, VX-548 – 14.1 (A). Representative I-t plots are shown in B.
Blinded assessment of hNaV1.9 pharmacology using a spiked plated approach
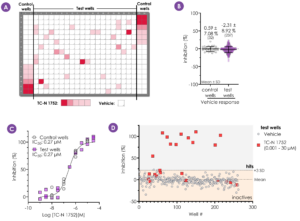
Figure 6 - The robustness of the Qube 384 assay was further validated by assessing the potency of TC-N 1752, using a randomised spiked plate approach (plate map - A). Vehicle response and TC-N 1752 potency correlated well between control and test wells (B, C). In test wells, the vehicle response displayed low variability with the TC-N 1752 response (at >0.1 µM) easily discernible above mean vehicle response + 3 SD threshold (D).