GLP-compliant hERG testing is a requirement under the ICH S7B guidelines, which mandate that certain safety pharmacology studies, including those assessing a drug’s potential interaction with the hERG potassium channel, must adhere to Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) principles.
According to these guidelines:
- In vitro IKr assays (which assess the blocking potential of the hERG channel) must be conducted using GLP-compliant methods.
- In vivo QT assays are also required to follow GLP-compliant standards when submitted for regulatory approval.
hERG testing is a critical component of preclinical safety pharmacology studies required for Investigational New Drug (IND) applications. It ensures that:
- Data regarding a drug’s potential to cause cardiac arrhythmias is reliable and consistent.
- The risk of serious complications, such as Torsades de Pointes (TdP), is identified early.
- Confidence is built in a drug’s safety profile, supporting regulatory decision-making processes.
Our hERG testing services have been:
- Audited and approved by the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA).
- Aligned with best practices set by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
These audits and accreditations highlight the quality and reliability of our services, reaffirming that we operate in full compliance with the highest regulatory standards.
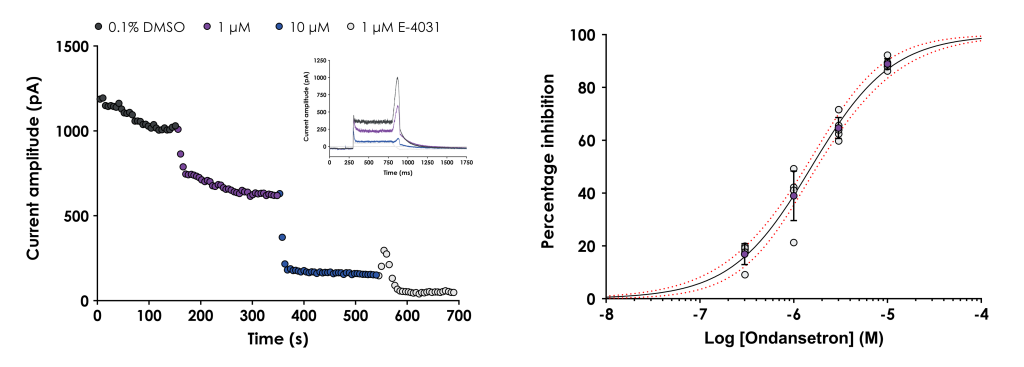
Figure 1. A. Graph showing the peak hERG tail current plotted against time for a representative cell treated with 1 and 10 μM ondansetron followed by 1 μM E-4031. The inset figure shows representative current traces in 0.1% DMSO, ondansetron and E-4031. B. Graph showing the mean ± SD inhibition data (purple symbols), as well as individual inhibition values (grey symbols), plotted against concentration. The data were fitted with a Hill equation to yield the half-maximal inhibition concentration (IC50) and the 95% confidence bands (red dashed lines).
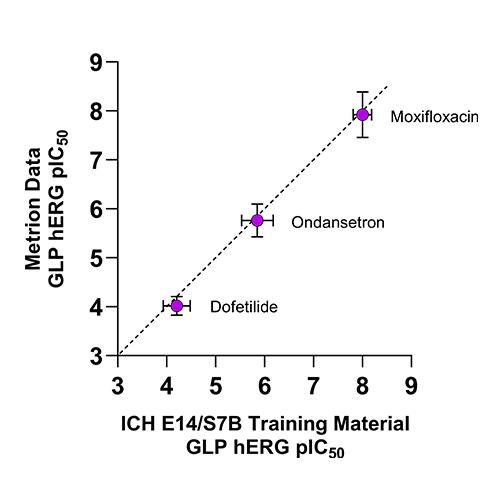
Figure 2. Comparison of GLP hERG IC50 values from Metrion versus published ICH E14/S7B training material values.


