Collaborative drug discovery for ion channel screening
Contract Research Organisations (CROs) Domainex and Metrion have formed a collaborative drug discovery partnership to identify novel chemical hits against ion-channel targets. Key to this collaboration are Domainex’s experience in hit identification and Metrion Bioscience’s expertise in ion channel screening and pharmacology. Both partners bring their extensive knowledge of drug target screening.
The transient receptor potential cation channel A1 (TRPA1) is a voltage-dependent, non-selective cation channel that plays a crucial role in sensory processes, particularly in the detection of noxious stimuli such as irritants and chemicals. It is an established therapeutic target, as antagonists of TRPA1 may have significant utility in the treatment of pain, chronic cough, and other inflammatory conditions. Due to its involvement in mediating pain and inflammatory responses, TRPA1 has been a focus of drug development efforts aimed at alleviating various chronic conditions, including neuropathic pain, asthma, and irritable bowel syndrome. Bautista et al.¹ described TRPA1 as a ‘gatekeeper of chronic inflammatory disorders of the skin, airways, and gastrointestinal tract’, highlighting its importance in managing a broad spectrum of inflammatory disorders and making it a key target for therapeutic intervention.
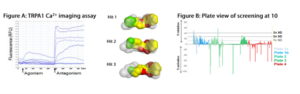
As part of this collaboration, Domainex applied its proprietary LeadBuilder platform to identify commercial compounds for screening based on Metrion’s validated agonist and antagonist profiles of reference compounds. Compounds were then purchased and screened at Metrion through an extensive cascade of assays, to identify true antagonists of the TRPA1 ion channel, with the ultimate goal of advancing the development of novel therapeutic agents targeting this critical ion channel, which plays a pivotal role in various physiological processes, including pain sensation and inflammation.