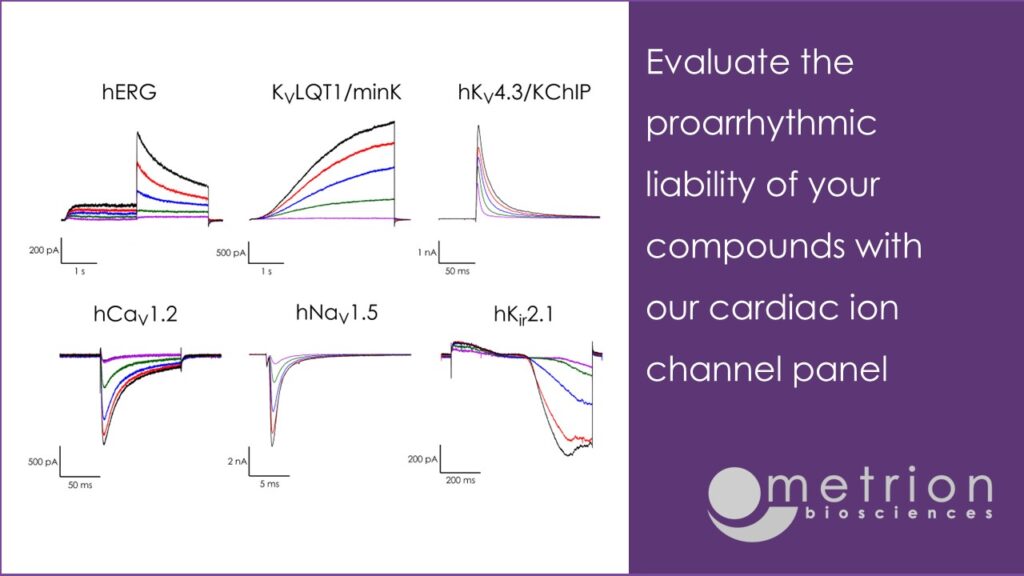
The cardiac late Na+ current (late INa) generates persistent inward currents throughout the plateau phase of the ventricular action potential and is an important determinant of repolarisation rate, EADs and arrythmia risk¹. As inhibition of late INa can offset drug effects on hERG and other repolarising K⁺conductances, it is one of the key cardiac channels in the Comprehensive in vitro Pro-arrythmia Assay (CiPA) panel being developed by the FDA to improve human clinical arrythmia risk assessment²̛ ³.