Jacob describes his work at Metrion, the technologies he used and how they complemented his PhD research.
The high-throughput screening of vast numbers of compounds is pivotal to the drug discovery process. It is often an expensive and time-consuming process, which can return false positive results. What sets us apart is our specific high-throughput screening knowledge and broad experience across multiple ion channel targets, enabling us to generate reliable, reproducible data and reduce the risk of costly downstream failures.
 Our ion channel high-throughput screening specialists can support with hit-finding campaigns, hit-to-lead activities, and lead optimisation, with follow-up selectivity profiling.
Our ion channel high-throughput screening specialists can support with hit-finding campaigns, hit-to-lead activities, and lead optimisation, with follow-up selectivity profiling.
Your project will be led by a Leadership Team with over 125 years of combined drug discovery experience, predominantly in the ion channel field. Once we have run your project, we will interpret the data, communicate the results clearly, and support your decision-making to best inform your screening strategy and accelerate development timelines.
Our complementary phenotypic and translational assays enable further, detailed characterisation of your lead compounds, helping you make informed choices in progressing your drug discovery programme with confidence and scientific rigour.
Custom cell line generation, assay development, and optimisation are also provided in-house, ensuring a seamless, integrated approach tailored to your unique programme goals.
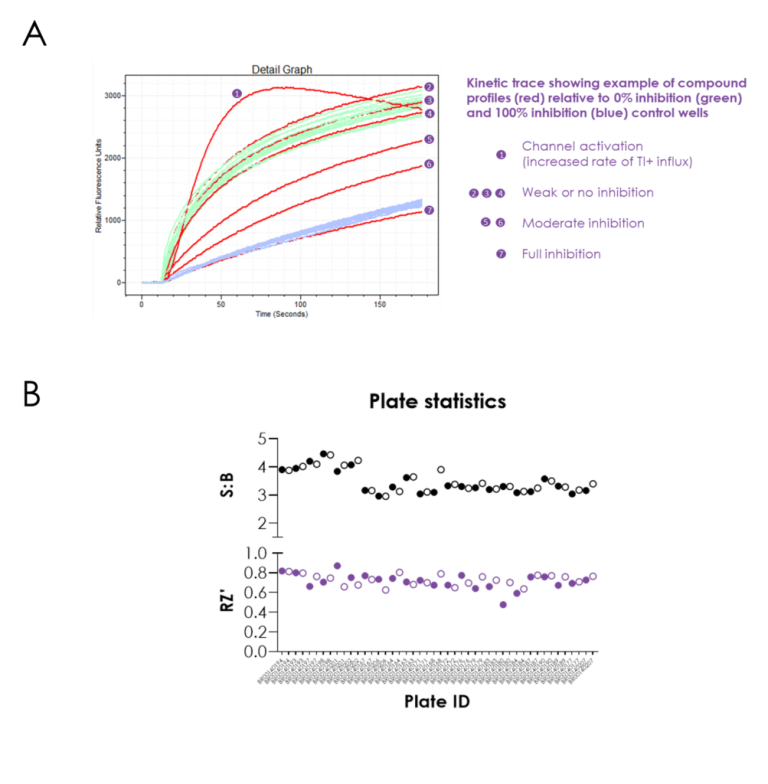
Figure 1. Screening against V434L KCNC1 using thallium flux assay. Read the drug repurposing high-throughput screeningcase study about a recent project researching a rare de novo variant in the KCNC1 gene.
To support your medicinal chemistry programmes and structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies, we offer access to commercially available compound libraries from Enamine and Assay.Works.
Metrion partnered with The KCNC1 Foundation and Perlera to carry out a high-throughput screen of a drug repurposing library aimed at identifying new therapeutic uses for existing approved drugs. This approach enabled Metrion to help identify potential treatments with established safety profiles, allowing therapies to be developed faster and more cost-effectively than through traditional drug discovery methods.

Figure 2: Physico-chemical property profile of Assay.Works library according to Lipinski’s Rule of 5 (left); Prediction of compound properties and drug-like features: Colloidal Aggregation, Permeability, Bioavailability, Solubility, PAINS.

Figure 3: Assay.Works compound sets and diversity metrics based on Bemis-Murcko clusters.
Jacob describes his work at Metrion, the technologies he used and how they complemented his PhD research.
Nicole describes her work at Metrion, the technologies she used and how they complemented her PhD research.