Understanding cardiac safety early is critical in drug development. In their latest poster, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, explain how they utilised Metrion’s clinically translatable cardiotoxicity assay to do exactly that.
 Enhance predictive accuracy, reduce false negatives and late-stage failures for safer drug development with improved preclinical-to-clinical translation
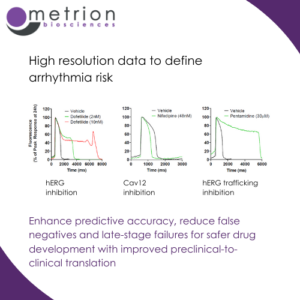
Enhance predictive accuracy, reduce false negatives and late-stage failures for safer drug development with improved preclinical-to-clinical translationRecordings using voltage-sensitive dye (VSD) with quality equivalent to patch-clamp are crucial for assessing cardiovascular risk in drug discovery. They provide a high-fidelity, high-throughput alternative to traditional electrophysiology techniques.
VSD-based recordings offer non-invasive, high-resolution measurements of membrane potential changes across a large number of cells or wells simultaneously, enabling faster and more efficient cardiac safety screening. This approach ensures precise detection of drug-induced effects on cardiac ion channels, such as hERG (IKr), Nav1.5, and Cav1.2, which are critical for evaluating proarrhythmic risk.
The ability to achieve patch-clamp-equivalent data quality using VSD enhances predictive accuracy, reducing false negatives and late-stage failures, and supports safer drug development with improved preclinical-to-clinical translation.
Read more about our hiPSC cardiomyocyte assay.
Understanding cardiac safety early is critical in drug development. In their latest poster, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, explain how they utilised Metrion’s clinically translatable cardiotoxicity assay to do exactly that.
Aligos Therapeutics and Metrion explore key approaches to cardiovascular safety screening in drug discovery.