Using automated patch clamp technology, we evaluate the potency and selectivity of ten Nav1.7-selective arachnid peptide toxins, which have been fused to the C-terminus (Fc region) of human IgG1.
 Enhance the predictive accuracy of cardiac safety assessments to ensure safer drug development and reduce the likelihood of late-stage failures due to cardiac toxicity
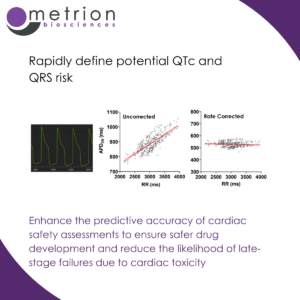
Enhance the predictive accuracy of cardiac safety assessments to ensure safer drug development and reduce the likelihood of late-stage failures due to cardiac toxicityEvaluating multiple endpoints including APD20/50/90 (action potential duration at different repolarisation stages), rise time, beat rate, and triangulation is crucial for assessing cardiovascular risk in drug discovery. It provides a comprehensive understanding of a compound's effects on cardiac electrophysiology. These endpoints collectively help identify proarrhythmic risks by detecting subtle changes in ion channel function that may not be apparent from a single parameter. APD20/50/90 measurements assess repolarisation dynamics, crucial for detecting the risk of QTc prolongation risks and early afterdepolarizations (EADs. Rise time reflects sodium channel activity and depolarization efficiency, while beat rate monitors drug-induced chronotropic effects. Triangulation (the difference between APD90 and APD30) is a key indicator of repolarization instability linked to Torsades de Pointes (TdP) risk.
By analysing multiple endpoints simultaneously, researchers can enhance the predictive accuracy of cardiac safety assessments, ensuring safer drug development and reducing the likelihood of late-stage failures due to cardiac toxicity.
Read more about our hiPSC cardiomyocyte assay.
Using automated patch clamp technology, we evaluate the potency and selectivity of ten Nav1.7-selective arachnid peptide toxins, which have been fused to the C-terminus (Fc region) of human IgG1.
Understanding cardiac safety early is critical in drug development. In their latest poster, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, explain how they utilised Metrion’s clinically translatable cardiotoxicity assay to do exactly that.