CiPA logoThe International Council on Harmonization (ICH) S7B and E14 regulatory guidelines were introduced in 2005 to evaluate the proarrhythmic liability of new drugs.
Evaluate the effect of compounds on action potentials recorded from hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes using conventional manual patch clamp methodology.
Spontaneous or evoked action potentials can be recorded and used to determine the effect of compounds on a range of action potential parameters. The recordings are stable for >30 minutes, which allows the cumulative application of multiple concentrations of each compound.
The manual patch clamp assay generates high fidelity recordings that allow the detection of even subtle changes to the action potential waveform. This helps to successfully discern between compounds with low, medium and high proarrhythmic risk profiles. For example, the figures below show mean data generated using 50 nM dofetilide, which reveals a significant prolongation of all measured APD values.
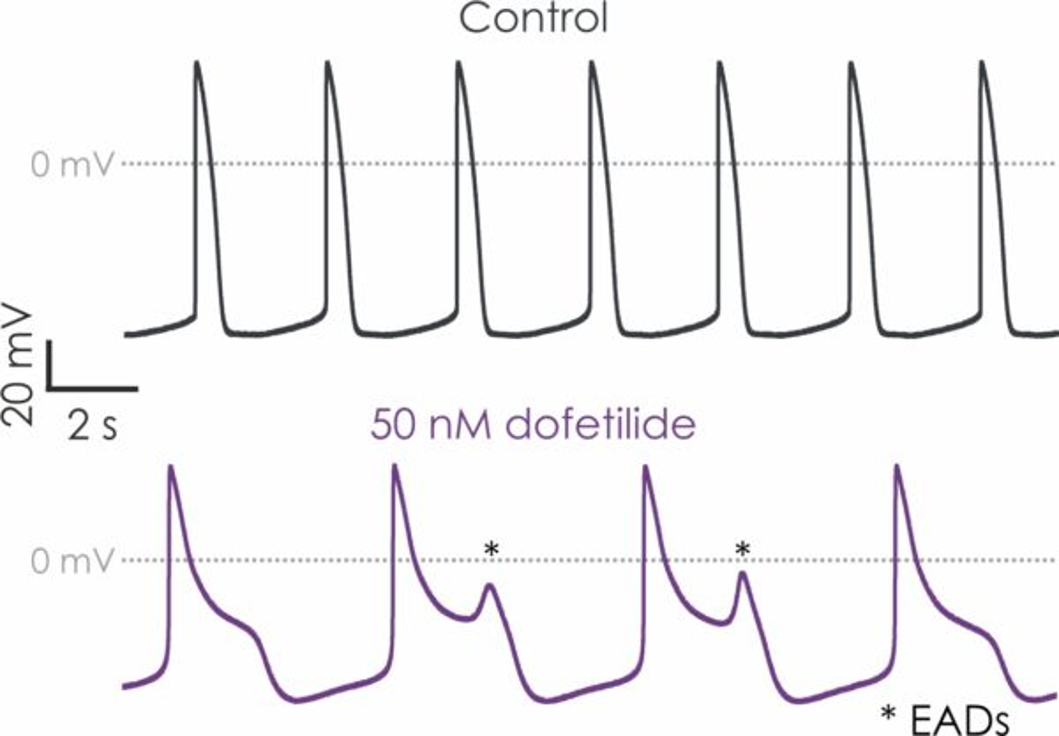
Figure 1. hiPSC-derived cardiomyocyte action potential screening.

Figure 2. Drug effects on hiPSC-derived cardiomyocyte responses.

Figure 3. Changes in hiPSC-derived cardiomyocyte beat stability.
CiPA logoThe International Council on Harmonization (ICH) S7B and E14 regulatory guidelines were introduced in 2005 to evaluate the proarrhythmic liability of new drugs.
In light of the FDA’s changing stance, the Volta assay emerges as a powerful, validated NAM capable of addressing the very safety concerns traditionally assessed in animal studies.